What is the Distortion Zone?

Bend allowance is simply a "keep out"
Why is the Distortion Zone Important?
Accurate Fabrication: Distortion Zones play a crucial role in the accuracy of sheet metal parts. Without proper accommodation, the final product may deviate from the intended design, leading to misalignments and assembly issues. By accounting for the distortion zone, designers can ensure that the part fits perfectly within the assembly, reducing the need for costly rework.
Material Efficiency: One of the primary concerns in sheet metal design is material utilization. Incorrect distortion zone accommodation can lead to material wastage by cutting parts that do not fit the design specifications.
Consistent Production: In mass production, consistency is key. Accounting for distortion zones help in maintaining uniformity across multiple parts, ensuring that each piece meets the required specifications. This is especially important in industries like automotive, where thousands of identical parts are produced, and any deviation can lead to significant issues in the final product.
Time Efficiency: Accurate distortion zone accommodation saves time in both the design and manufacturing phases. Designers can create precise drawings without the need for extensive trial and error. In the manufacturing phase, it ensures that parts are produced correctly on the first attempt, reducing the need for adjustments and rework.
Cost Reduction: By ensuring accurate fabrication, material efficiency, and consistent production, accounting for distortion zones directly contributes to cost reduction. Fewer errors mean less waste and rework, and optimized material usage reduces the overall cost of production. This makes distortion zones a critical factor in keeping manufacturing costs under control.


Factors Affecting Distortion Zone
Several factors influence the size of the distortion zone.
- Material Thickness: Thicker materials require more allowance due to the increased distance that the neutral axis must travel during bending.
- Bend Radius: A smaller bend radius increases the amount of stretching on the outer surface, requiring more allowance.
- Material Type: Different materials have varying levels of elasticity and ductility, which can affect how they behave during bending.
How to account for the Distortion Zone
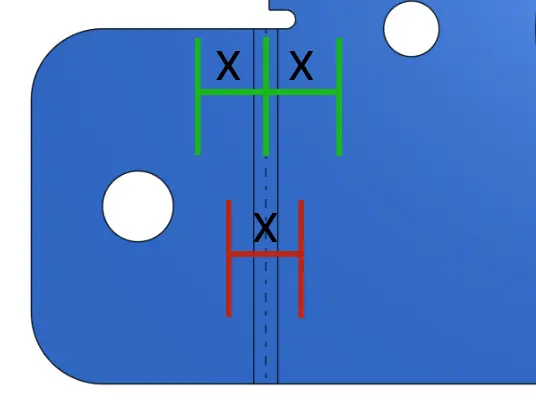
The distortion zone is simply a distance in both directions from the bend line that you can consider "keep out" zone. As long as your keep your critical features outside of this area distortion will not change their dimensions. If you are having your parts bent through the Fabworks Bending Service you can reference the Material Table on the Bending Guidelines page to know how far from bend lines to keep clear. If you are bending parts yourself it might be best to experiment on scrap material, and make your own distortion zone table.
Important:
How to Manipulate the Distortion Zone
The easiest way to prevent the distortion zone from interfering with features is to place those features far enough away from the bends. However sometimes this is not possible. In the case of a part with a feature very close to the bend line you can add a slit in the part to prevent that section from bending, just keep in mind this does reduce the strength of the part. See this in action here.
Conclusion
The distortion zone is an essential consideration in sheet metal design, influencing everything from accuracy and material efficiency to production consistency and cost. By understanding and applying the correct distortion zone, designers and manufacturers can ensure high-quality, durable products that meet precise specifications.
What is K-Factor?
Demystify K-factor in sheet metal bending. Learn its importance and how Fabworks ensures precise bends without complex calculations.
Fast Track Your Project .
Seamless process, unparalleled precision, unbeatable speed. Turn your design into reality by beginning your journey with us today.
or drag and drop
.STEP / .STP up to 25MB
Your file are safe, secure and retain all intellectual rights.